Blog
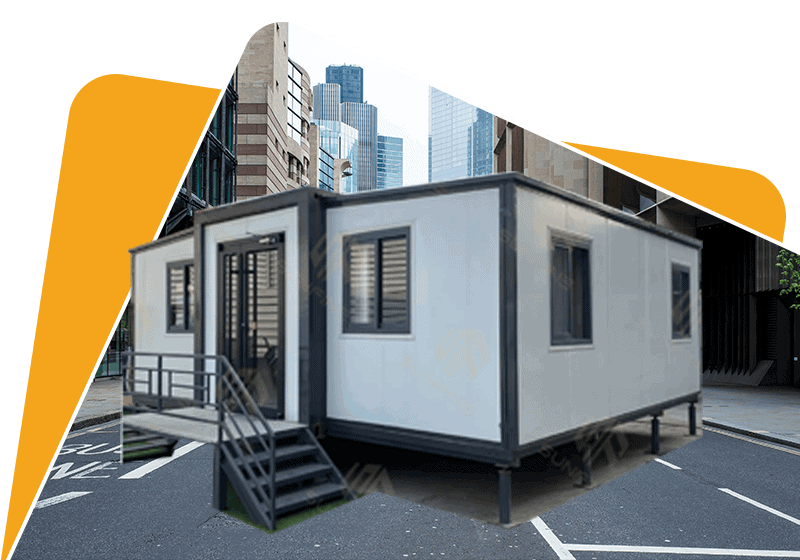
10 Popular Questions About Heavy Duty Cabin

10 Popular Questions About Heavy Duty Cabin
- What are the different types of heavy duty cabins?
- What features should I look for when choosing a heavy duty cabin?
- How are heavy duty cabins constructed for durability?
- What kind of insulation works best for heavy duty cabins?
- What size heavy duty cabin do I need?
- What are the best uses for a heavy duty cabin?
- How much does a heavy duty cabin cost?
- What are the pros and cons of DIY vs prefabricated heavy duty cabins?
- How difficult is it to assemble a heavy duty cabin kit?
- What kind of foundation is best for a heavy duty cabin?
What are the different types of heavy duty cabins?
When it comes to heavy duty cabins, there are a few main types to consider:
- Log cabins – These iconic cabins are constructed from solid timber logs, usually pine, cedar or spruce. The thick log walls provide excellent insulation and durability. Log cabins have a classic, rustic aesthetic.
- Timber frame cabins – A timber frame uses large timber posts and beams connected with joinery, then enclosed with exterior siding and interior drywall. The post and beam structure is strong and can support multi-story cabins.
- Steel frame cabins – With a welded steel frame clad in steel siding, these cabins are extremely sturdy and weather-resistant. The prefabricated panels make for faster assembly.
- Concrete cabins – Concrete is poured into forms to create the walls and floor of the cabin. Concrete has exceptional thermal mass to regulate interior temperatures. These modern cabins have a unique look.
- Hybrid cabins – Many heavy duty cabins combine different materials like logs and timber or steel frame with log accents. This allows builders to utilize the benefits of each material.
The type of heavy duty cabin depends on the location, intended use, budget and aesthetic preferences. Log and timber options provide a more traditional look, while steel and concrete offer increased durability and energy efficiency.
What features should I look for when choosing a heavy duty cabin?
When selecting a heavy duty cabin, there are several key features to evaluate based on your needs:
- Insulation – A well-insulated cabin will maintain livable interior temperatures year-round. Look for thick walls packed with fiberglass or foam insulation. Thermal pane windows and insulated doors are also important.
- Ventilation – Proper ventilation is crucial to control humidity and let fresh air circulate. Operable skylights, ridge vents and eave vents are very helpful. Ceiling fans also improve air flow.
- Foundation – A sturdy foundation like a concrete slab, pier footings or raised wood subfloor will provide stability and prevent shifting. Make sure it is rated for your area’s frost line depth.
- Frame – The frame should be constructed from durable, rot-resistant materials like pressure-treated lumber, steel or concrete. This provides structural integrity.
- Exterior – Heavy duty siding like log, plank, stucco, brick or steel protects against weather and pests. Consider snow load capacity for roofing.
- Utilities – Off-grid cabins need solar panels, generators and propane. Or choose hook-ups for electricity, water and septic if available.
- Storage – Built-in space for gear, equipment and pantry storage is useful. Lofts, closets, shelving and exterior sheds add functional space.
Prioritize insulation, ventilation and a sturdy foundation when choosing your ideal heavy duty cabin. Also consider the framing, utilities and your storage needs.
How are heavy duty cabins constructed for durability?
Heavy duty cabins are specially constructed to withstand the elements and provide lasting shelter and security far beyond a typical residential home. Here are some of the key methods used:
- Thick, reinforced framing – Posts, beams and rafters are larger dimensional lumber or steel, secured with robust brackets and hardware. This creates a stronger frame less prone to sagging.
- Multi-layered sheathing – The exterior walls and roof are built up with two or more layers of structural sheathing like plywood or OSB. This adds lateral strength.
- Closer frame spacing – Studs, joists and rafters are spaced more narrowly, usually 12″ to 16″ on center rather than 24″. This distributes loads better.
- Steel roofing – Metal roofing like standing seam steel resists damage from falling branches, snow accumulation and high winds.
- Impact-resistant siding – Heavy duty plank, logs or steel siding is used instead of vinyl or fiber cement. This protects against hail, falling debris and animals.
- Reinforced connections – Hurricane clips, structural screws and construction adhesive create robust connections to resist wind uplift.
- Waterproofing – Membrane waterproofing on the foundation and under the siding prevents moisture intrusion that could cause rot.
- Termite treatment – Treating all lumber in the framing and additional barriers prevents termite infestations from compromising the structure.
Following these best practices allows heavy duty cabins to stand up to the demands of full-time occupancy in remote locations and harsh climates.
What kind of insulation works best for heavy duty cabins?
Heavy duty cabins require insulation with excellent thermal performance to handle cold winters and make the most of heating fuel. Here are some top insulation options:
- Spray foam – This polyurethane foam expands to fill every gap and dries rigid. It has an insulation value around R-6 per inch and also air seals. Closed-cell is more expensive but denser and water resistant.
- Rigid foam – Rigid foam panels of XPS or EPS can achieve R-5 per inch. They are moisture resistant and great for a continuous layer over walls and under floors. Use adhesive and mechanical fasteners to attach.
- Fiberglass batts – Traditional fiberglass batt insulation is cost-effective and provides good sound dampening. Look for batts rated R-13 to R-15 for 2×4 walls and R-30+ for attics. Use with a vapor barrier.
- Mineral wool – Made from natural basalt or slag, mineral wool has similar insulation properties as fiberglass. It is fire resistant and handles moisture well.
- Cellulose – Treated recycled paper fiber can be blown into wall cavities at high density for R-3.5 per inch. It reduces air leakage effectively.
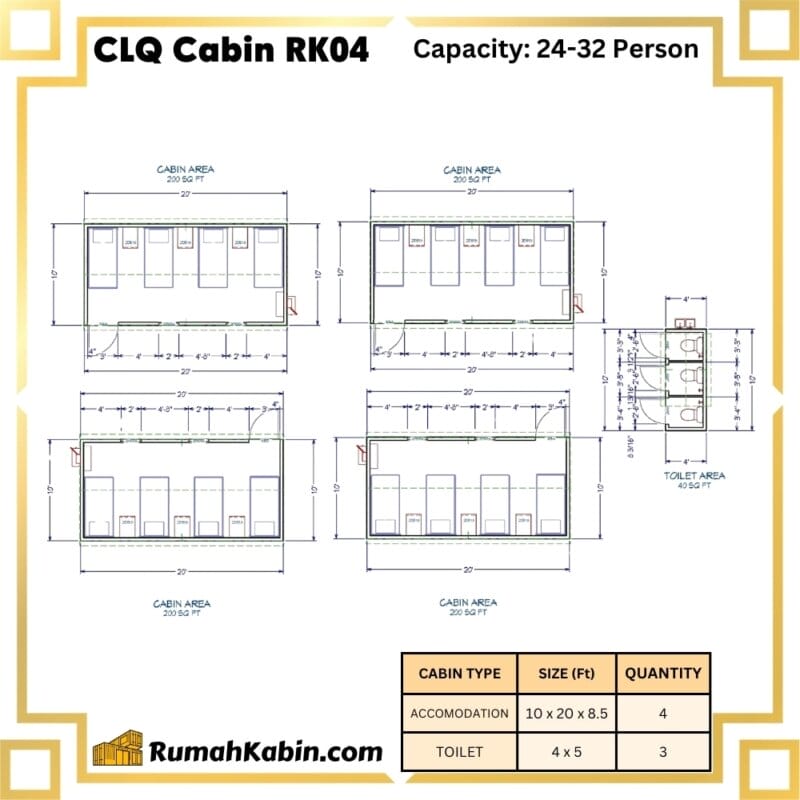
What size heavy duty cabin do I need?
Determining the right size heavy duty cabin depends on your intended use, budget and how much space you need. Here are some tips:
- List all the functions the cabin needs to accommodate like sleeping, cooking, bathing, storage, etc.
- Consider how many people need to sleep there. Allow 50-60 sq ft per person for comfortable full-time living.
- Include desired amenities like a full kitchen, washer/dryer, wood stove, desk space, etc. These take up footprint.
- Lofts can add sleeping space without increasing the foundation size. But allow room for ladders to access the loft.
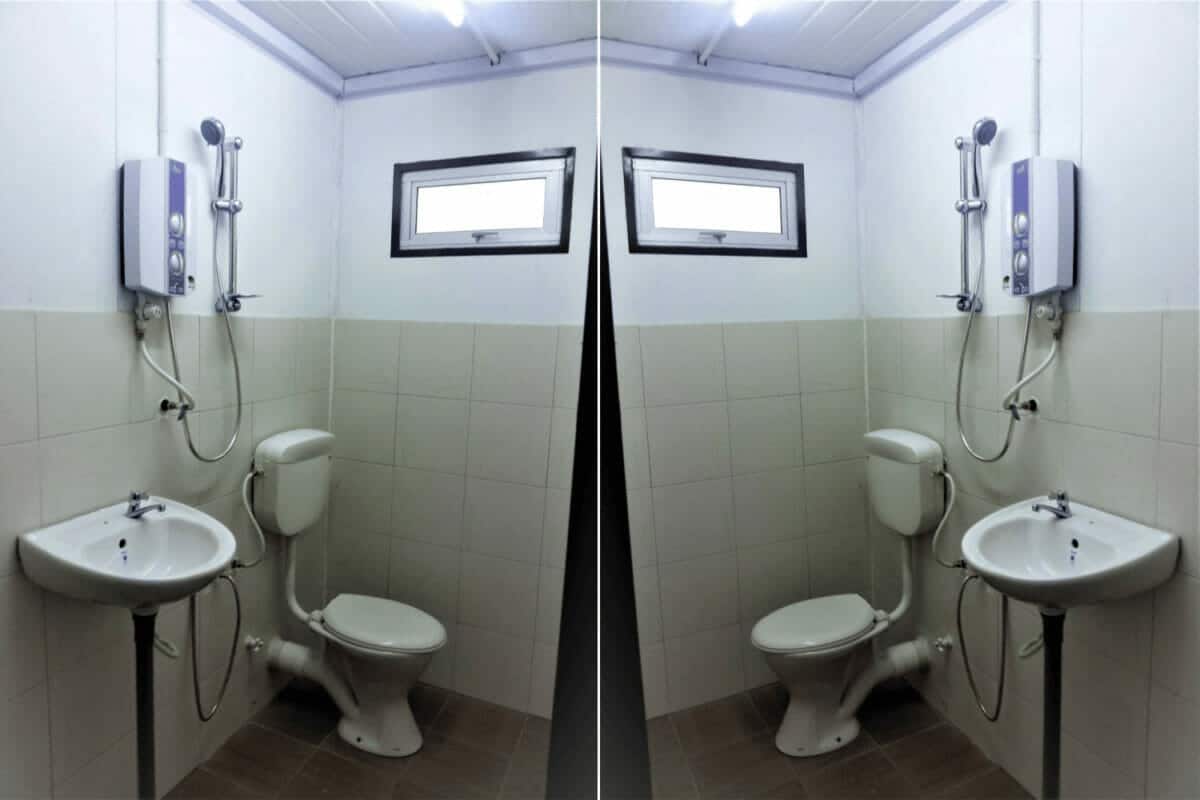
- Bathrooms require 20-25 sq ft for a toilet/shower stall. Composting toilets are smaller.
- Kitchens need at least 50 sq ft for cabinets, appliances and prep space.
- Add a mudroom, porches or deck to transition indoors/outdoors and store gear.
- Plan storage for equipment, tools, pantry food, linens, clothes and other essentials.
- Allow space to move around furnishings without feeling cramped, at least 5-7 feet between.
- Consider potential future needs like additional family members or functions. Size up if possible.
Heavy duty cabins under 500 sq ft work well for 1-2 people. Go up to 800+ sq ft for larger families or to accommodate more activities.
What are the best uses for a heavy duty cabin?
Heavy duty cabins are extremely versatile and great for many applications thanks to their rugged construction. Here are some top uses:
- Permanent Home – They make for spacious, durable full-time residences in remote, cold weather locales from Alaska to Montana to Maine.
- Hunting/Fishing Cabin – Use as a seasonal base camp for hunting, ice fishing or other wilderness hobbies in any climate.
- Off-the-Grid Retreat – Escape modern life and live self-sufficiently with a heavy duty energy-efficient cabin.
- Rental Income Property – Rent out your cabin nightly or weekly in a vacation area for profitable income potential.
- Guest House – Accommodate visiting friends and family with this separate dwelling on your property.
- Home Office – Use your cabin as a quiet, comfortable workspace if you work from home.
- Pool House – Enjoy a relaxing hangout by your pool with a nearby heavy duty pool house for changing clothes, cooking and lounging.
- Teen/In-Law Suite – These cabins work great as a separate living space for relatives or older kids.
Heavy duty cabins offer incredible flexibility. Whether for full-time occupancy or a part-time recreational retreat, they provide lasting value and enjoyment.
How much does a heavy duty cabin cost?
The cost for a heavy duty cabin can vary quite a bit based on the size, materials, level of customization and finishing touches. Here are some typical price ranges:
- Prefab kit cabins – Basic kits for a 200-400 sq ft cabin with plywood siding start around $15,000 – $30,000. Larger kit cabins are $50,000+.
- Log cabin kits – Hand-peeled or milled log kits for a 20×20 cabin run $40,000 – $80,000 depending on log thickness. Larger sizes with added porches, lofts, etc can reach well over $100,000.
- Timber frame cabin kits – Expect $30,000 – $50,000 for a basic 20×20 timber frame shell. Elaborate designs are $70,000-$150,000.
- DIY build – If you have carpentry skills, building your own basic cabin from plans can cost $20,000 – $35,000 in materials to frame up a 200 sq ft space.
- Turnkey installed – Having a cabin fully built onsite by a contractor raises costs to $50,000 – $250,000+ depending on amenities.
- Foundation & utilities – Budget $15,000 – $30,000 for site prep, foundation, septic, and installing power, water and HVAC.
Prioritize insulation, waterproofing and durable materials when investing in your heavy duty cabin for many years of rugged performance.
What are the pros and cons of DIY vs prefabricated heavy duty cabins?
Deciding between a DIY build or prefab kit comes down to your skills, time and budget. Here are some pros and cons to weigh:
DIY Cabin
Pros:
- Customize every aspect like size, layout, materials
- Potentially lower cost by acting as own contractor
- Learn useful construction skills
- Make improvements/repairs yourself
Cons:
- Requires carpentry and building expertise
- Very time consuming to build from scratch
- Need to source all materials individually
- Difficult to build off-grid
- Permitting/inspections may be complex
Prefab Cabin
Pros:
- Very fast installation, often in 1-2 days
- No construction skills needed
- Everything included in one kit
- Professional design and craftsmanship
- Many customization options
Cons:
- Limited size and layout options
- Cannot make changes or additions
- Must be installed properly on foundation
- More expensive upfront cost
- Delivery logistics may be difficult
For most homeowners, a prefab heavy duty cabin kit offers convenience and quality at a reasonable price. But DIY builds allow for total customization if you have the skills.
How difficult is it to assemble a heavy duty cabin kit?
Assembling a prefab heavy duty cabin kit is made to be relatively straightforward for homeowners without professional construction experience. Here are some tips for smooth assembly:
- Review the instruction manual thoroughly before starting. Some steps must be completed in order.
- Ensure the foundation is prepared with anchor points for securing the cabin.
- Have all tools like impact drivers, ladders, saws, and drills ready to go. A lifting boom may be needed.
- Recruit 2-3 helpers for lifting wall panels and holding components in place. More hands make the work easier.
- Take your time measuring and checking for square as each section is put together. Attention to detail prevents issues.
- Follow instructions closely when installing windows, doors, roofing and siding. Proper weatherproofing is crucial.
- Allow a full week for assembly. Complex kits with lofts or porches take longer. Don’t rush.
- Contact the manufacturer for support
What kind of foundation is best for a heavy duty cabin?
A proper foundation is key to the structural integrity and longevity of a heavy duty cabin. Here are some of the best foundation options:
- Concrete slab – Poured concrete slabs are the strongest option. They need proper drainage and reinforcement with rebar or fiber mesh. At least 6″ thick. Insulate the slab edge.
- Pier and beam – Helical or concrete piers anchored deep into the ground hold up perimeter beams. Allows for airflow underneath.
- Raised subfloor – A wooden subfloor on a gravel base or pier footings elevates the cabin above ground. Provides space for plumbing.
- Stem wall – Concrete block stem walls create a reinforced perimeter to build floor framing on. They integrate well with slab and crawl space foundations.
- Screw piles – Steel screw anchors drilled deep into the ground secure the cabin against uplift and shifting. Best for places with permafrost.
- Grading – The ground must slope away from the cabin for drainage. If not, build up with fill or gravel.
- Frost line – In cold climates, foundations need to extend below the frost line to prevent heaving. Typically 4+ feet.
Take time to prepare the site and install the right heavy duty cabin foundation. This provides long-lasting structural support and keeps the interior comfortable.
Key Takeaways:
- Heavy duty cabins are available in log, timber, steel and concrete builds to withstand harsh weather and frequent use.
- Prioritize insulation, ventilation and foundation when selecting a heavy duty cabin. Also consider storage needs.
- Thick framing, multi-layer sheathing and reinforced connections add durability.
- Spray foam, rigid foam panels and dense-pack cellulose are great insulators for cabins.
- Under 500 sq ft works well for 1-2 people. Allow 50-60 sq ft per additional person.
- Use heavy duty cabins for permanent homes, recreational retreats, rental income and more.
- Prefab kits offer fast assembly while DIY builds provide total customization.
- Cabin costs range from $15,000 for basic prefab kits up to $250,000 for luxury installed cabins.
- Proper foundation options include concrete slabs, pier and beam, stem walls and screw piles.
Conclusion:
- Heavy duty cabins are specially constructed to provide lasting, durable shelter in remote areas and harsh climates.
- Choosing the right heavy duty cabin depends on your budget, space needs, location and intended use.
- Proper installation on an insulating foundation and building with multilayered sheathing and reinforced connections enables heavy duty cabins to stand up to frequent use and extreme weather.
- While prefab kits offer simplified assembly, custom DIY builds allow you to control all the details.
- Investing in a quality heavy duty cabin pays dividends for years to come with a rugged structure that supports your lifestyle.
Kontraktor Rumah Kabin
Rumah Kabin Murah
Rumah Kontena Vs Rumah Kabin
Rumah Kabin Pasang Siap
Senarai Harga Kabin di Malaysia
Heavy Duty Cabin
Light Duty Cabin